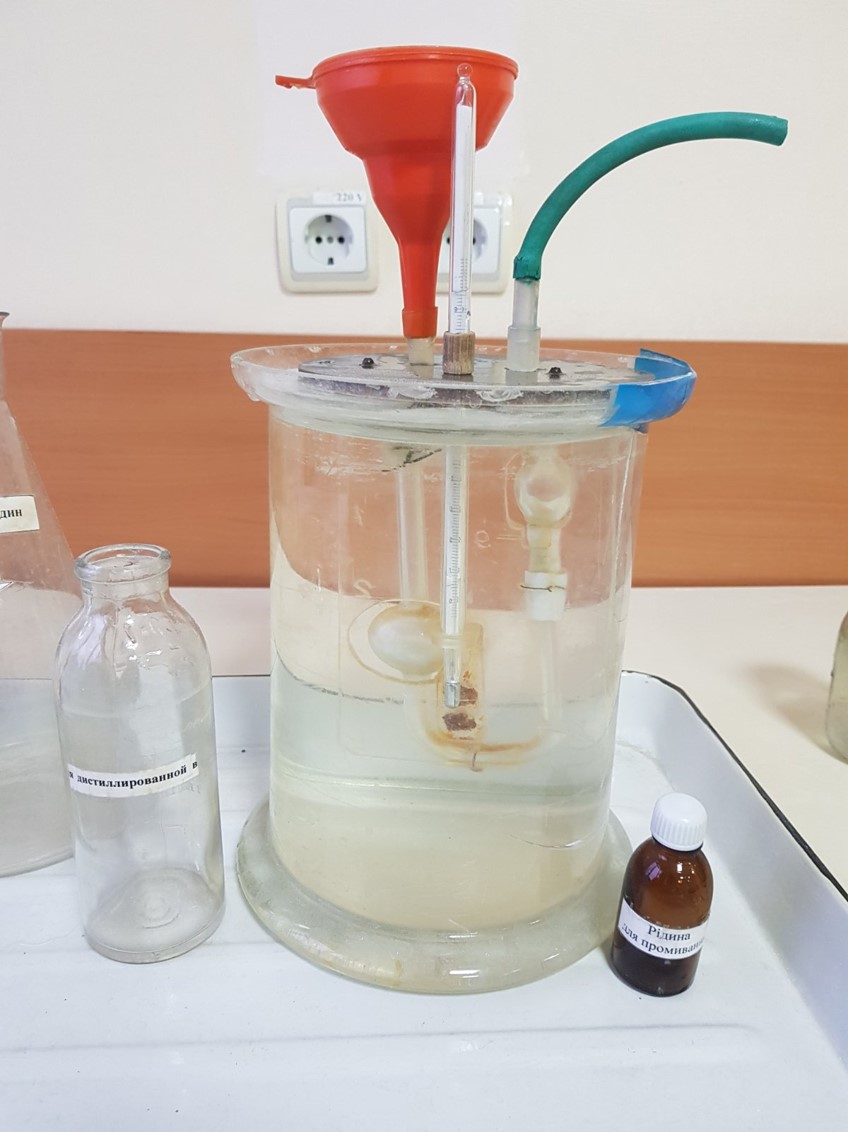
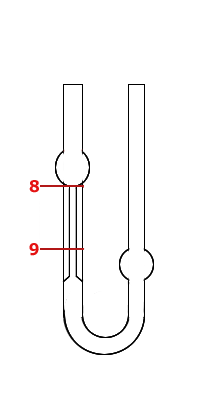
| № | Distilled water |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| t1= 24℃ | |||
| τ0, s |
|||
| ρ0 = 0,99733 kg/m3 |
η0 = 0,00091 N∙s/m2 |
|---|
| № | Distilled water + alcohol |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| t1= 24℃ | |||
| τx1, s |
|||
| ρx = 0,80741 kg/m3 |
ηx = ? N∙s/m2 |
|---|
| № | Distilled water + alcohol |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| t2= 32℃ | |||
| τx2, s |
|||